Table of Contents
ToggleThe terms syllabus and curriculum are often used interchangeably by students, but they have distinct meanings. A syllabus is a document that outlines the topics, objectives, and requirements of a specific course. In contrast, a curriculum refers to the overall set of courses, objectives, and educational experiences that comprise a programme of study.
In this blog, we provide an in-depth understanding of a Syllabus vs Curriculum to help clarify their differences.
What Do You Mean By Syllabus?
A syllabus is a document that outlines the objectives, expectations, and requirements of a course. The purpose of a syllabus is to provide clarity and transparency regarding topics covered in the course and the teaching and assessment patterns.
Components Of A Syllabus Typically Include The Following:
Course Description: This section provides an overview of the course, including the subject matter, course format, and any prerequisites or recommended background knowledge.
Learning Objectives: These are specific and measurable goals that students are expected to achieve by the end of the course. Learning objectives help students understand what they will be able to do as a result of taking the course.
Course Schedule: This outlines the weekly topics and assignments. It includes information about readings, lectures, assignments, and assessments.
Grading Policy: This section explains how the course will be graded, including the weighting of different assignments and assessments, the grading scale, and any policies regarding late work or missed assignments.
Course Policies: This section outlines any policies that are specific to the course, such as attendance requirements, classroom conduct, and academic integrity policies.
Examples Of Syllabus From Different Disciplines Might Include:
| Subject | Syllabus Content | Course Schedule |
| Biology | Cell biology, genetics, evolution, and ecology | Lab assignments and field trips to study local ecosystems |
| History | Different periods of history, such as Ancient Rome, the Renaissance, or World War II | Readings from primary sources and discussions of historical events |
| Mathematics | Calculus, linear algebra, and differential equations | Problem sets and quizzes to assess students’ understanding of mathematical concepts |
| Creative Writing | Different genres of writing, such as poetry, fiction, and creative nonfiction | Workshops where students share and critique each other’s writing |
What Do You Mean By Curriculum?
Curriculum refers to the set of courses, activities, and learning experiences that make up a specific educational programme. The purpose of a curriculum is to guide students towards achieving specific learning outcomes or goals. The curriculum is designed to ensure that students gain the knowledge, skills, and competencies necessary to succeed in their chosen field of study or career path.
Components Of A Curriculum Typically Include The Following:
| Component | Description |
| Learning Objectives and Goals | Define what students should achieve by the end of the programme. |
| Course Content | Topics and knowledge areas to be covered throughout the curriculum. |
| Teaching Methods | Instructional strategies like lectures, group discussions, and practical activities. |
| Assessment and Evaluation | Methods to measure student progress, such as exams, assignments, and projects. |
| Structure and Sequence | Organised progression of courses and topics, from foundational to advanced levels. |
There are different types of curriculum that institutions of higher education offer. General education curriculum are designed to provide students with a broad base of knowledge across different disciplines, while major-specific curriculum are focused on providing in-depth knowledge and skills in a particular area of study. Interdisciplinary curriculum combines multiple fields of study to create a unique learning experience that provides a more holistic understanding of a subject.
Examples Of Curriculum From Different Disciplines Might Include:
Examples of curriculum from universities differ significantly based on each institution’s educational philosophy, resources, and expertise. For instance:
- Liberal Arts Colleges: Focus on general education curriculum that emphasise the humanities and social sciences.
- Technical Schools: Prioritise major-specific curriculum with a strong focus on fields like engineering or computer science.
At Harvard University, the undergraduate curriculum is designed to provide a liberal arts education that exposes students to a wide range of subjects and disciplines. The curriculum includes distribution requirements in areas such as arts and humanities, social sciences, natural sciences and mathematics.
At the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), the curriculum is focused on STEM fields, with a strong emphasis on hands-on learning and research. MIT offers both major-specific and interdisciplinary curriculum, such as the Media Arts and Sciences programme, which combines computer science, engineering, and design.
At the University of California, Berkeley, the undergraduate curriculum includes both general education requirements and major-specific requirements. Berkeley’s interdisciplinary curriculum includes the Global Studies programme, which combines courses from various social science and humanities fields to provide a broad understanding of global issues.

Implications For Students
Syllabus and curriculum are vital tools for academic success, helping students plan, track, and achieve their goals.
Syllabus as a Roadmap: It outlines learning objectives, course schedules, and assignments, guiding students on what to expect and how to prepare. Reviewing it early helps manage time and workload effectively.
Curriculum for the Big Picture: It provides an overview of required courses and learning outcomes, allowing students to stay on track with programme requirements and explore electives aligned with their interests.
Strategies for Success:
- Review the syllabus and curriculum at the start of the semester and note important deadlines.
- Create a study schedule that aligns with course and programme requirements.
- Stay organised to reduce stress and improve performance.
Provide Feedback: Sharing feedback on the syllabus and curriculum through evaluations or discussions with instructors helps improve these tools for better learning experiences.
Implications For Educators
An effective syllabus and curriculum are essential tools for fostering student success. They provide clarity, set expectations, and ensure students gain relevant knowledge and skills.
Clarity and Structure: A well-designed syllabus guides students and eliminates confusion.
Engagement and Relevance: Updating curriculum keeps learning fresh, interactive, and aligned with real-world needs.
Continuous Improvement: Regular refinement addresses gaps and adapts to evolving trends.
Benefits Of Creating Effective Syllabus And Curriculum
A well-crafted syllabus and curriculum are the backbone of any successful educational programme. They not only set the tone for the learning journey but also act as a roadmap, guiding both educators and students toward achieving their goals. When thoughtfully designed, they offer clarity, consistency, and adaptability, creating a more engaging and impactful learning experience.
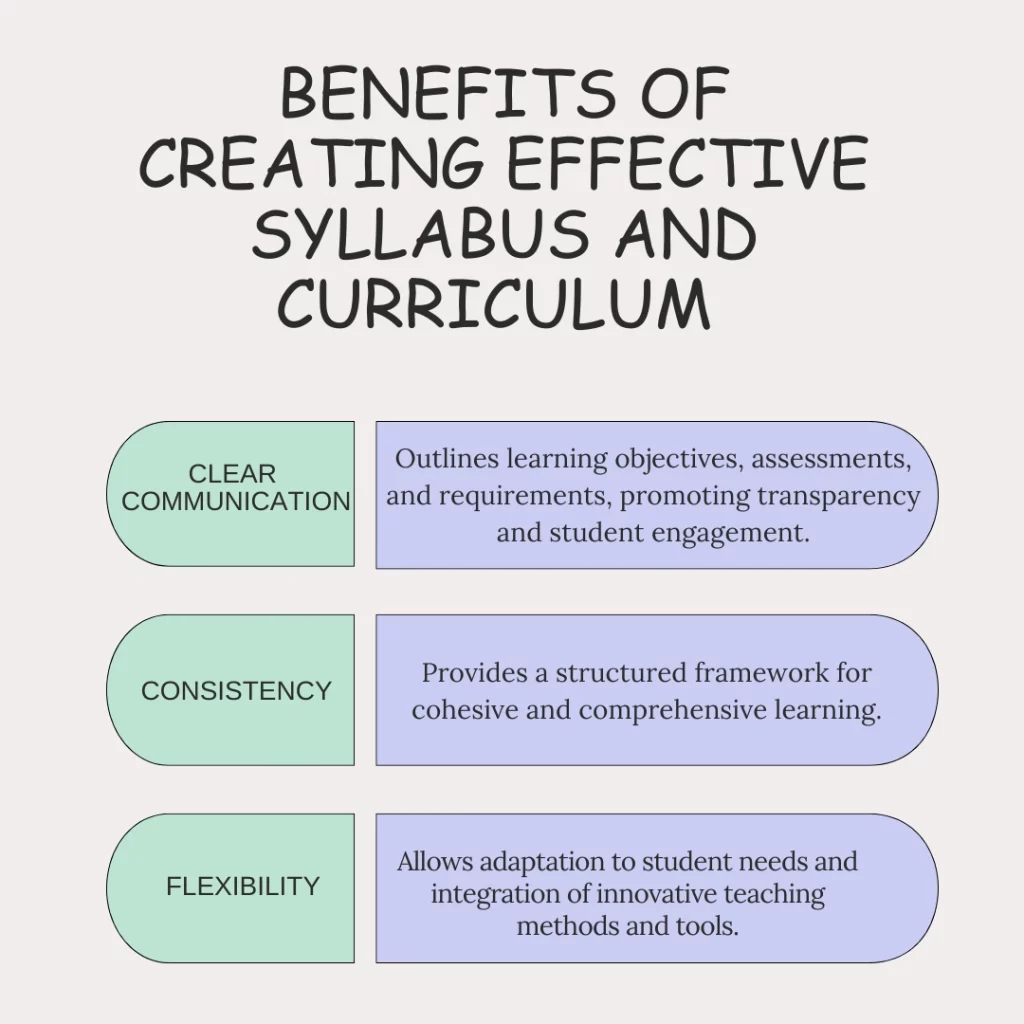
Strategies For Designing and Updating: Curriculum Vs Syllabus
Designing and updating a syllabus or curriculum requires thoughtful planning to ensure it meets both educational standards and student needs. By focusing on clear goals, relevant content, and engaging teaching methods, educators can create effective frameworks that enhance learning outcomes and keep pace with evolving academic and industry trends. Here’s how!
Alignment with Institutional and Disciplinary Standards: Educators should ensure that their syllabus and curriculum align with institutional and disciplinary standards. This ensures that students receive a high-quality education that meets the standards of the institution and their field of study.
Clear Learning Objectives: Educators should clearly define the learning objectives for their course or programme. This allows students to understand what they will be expected to learn and helps educators to design assessments that measure student progress toward these objectives.
Active Learning Strategies: Educators should incorporate active learning strategies into their syllabus and curriculum. This promotes student engagement and allows students to apply what they have learned to real-world situations.
Tips for Students and Educators
A syllabus and curriculum are essential for a successful academic journey. For students, they offer guidance on what to study and how to prepare. For educators, they provide a framework for delivering lessons effectively. Here are some simple tips to get the best out of them!
For Students:
Strategic Course Selection
- Research professors and course reviews before registration
- Balance challenging courses with more manageable ones each semester
- Choose electives that complement your major and build valuable skills
- Consider prerequisites for future courses when planning your schedule
Strategic Planning & Organisation
- Create a master calendar at the semester start, marking all major deadlines and exams
- Break down large assignments into smaller weekly tasks
- Use digital tools like Google Calendar or Notion to sync deadlines across devices
- Keep all course materials organised by subject in both digital and physical formats
Effective Time Management
- Block specific study times for each subject in your weekly schedule
- Use techniques like the Pomodoro method (25 minutes work, 5 minutes break)
- Designate “buffer days” before major assignments for unexpected issues
- Schedule regular review sessions instead of cramming before exams
For Educators
Curriculum Design Excellence
- Create clear learning pathways with measurable outcomes
- Include both theoretical foundations and practical applications
- Design assessments that test understanding rather than memorisation
- Incorporate learning material to accommodate different learning styles
- Build in flexibility for current events and emerging topics
Student Support & Engagement
- Schedule regular check-ins with students throughout the semester
- Create an inclusive classroom environment that welcomes different perspectives
- Provide additional resources for challenging topics
- Be accessible through multiple communication channels
- Enable a growth mindset among students
Technology Integration
- Use learning management systems effectively
- Incorporate relevant educational apps and tools
- Create accessible digital resources
- Implement analytics to track student progress
- Provide training resources for technology tools used in class
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between syllabus vs curriculum is essential for both students and educators. While a syllabus provides a detailed guide for individual courses, the curriculum serves as a broader framework for an entire academic programme. Together, they form the foundation for a structured, engaging, and effective educational experience. By focusing on clear objectives, active learning strategies, and adaptability, both students and educators can maximise the benefits of these educational roadmaps.
FAQs
What is the difference between curriculum and syllabus?
A syllabus outlines the content, expectations, and learning outcomes for a specific course, including topics, assignments, and grading policies. A curriculum is a broader framework that defines the learning objectives, scope, and sequence of courses for an entire programme of study.
What are the four basic curriculums?
The four basic curricula are Planning, Content and Methods, Implementation, and Evaluation and Reporting. These phases outline the curriculum development process, though real-world applications may not always align perfectly with the model.
Why is understanding the difference between syllabus and curriculum important for students?
It is important for students to understand the difference between a syllabus and a curriculum to plan their studies effectively. The syllabus helps them focus on course-specific requirements, while the curriculum provides a broader view of their academic and career goals. This distinction ensures they stay organised and aligned with both immediate and long-term objectives.
Can a syllabus and curriculum be changed mid-year?
Yes, both a syllabus and curriculum can be changed mid-year if necessary. However, any changes must be communicated clearly to students and other stakeholders, and the reasons for the changes should be explained.
Is it necessary to follow the syllabus and curriculum strictly?
Yes, following the syllabus and curriculum strictly ensures learning objectives are met, but flexibility may be needed for situations like accommodating disabilities or adapting to changes in the field.
Thank you for reading our blog on Understanding Universities: Syllabus vs Curriculum. We hope it provides valuable insights for prospective students. Don’t forget to explore our other blogs for more helpful information!


















1 thought on “Top PGDM Courses In Canada: Universities & Eligibility”
I have done Bachelor’s in Culinary Arts from India and completed my graduation in the year 2022 .I am 22 years old. After graduation, I have done 1 year paid internship from USA .Now, I would like to take occupational experience and learn culinary skills and also do masters in Culinary arts.How can I find the college n best course / country where I can persue studying further